Algorithm/알고리즘 문제 해결 전략
근거리 네트워크 (LAN)
Henu
2021. 7. 18. 19:25
algospot.com :: LAN
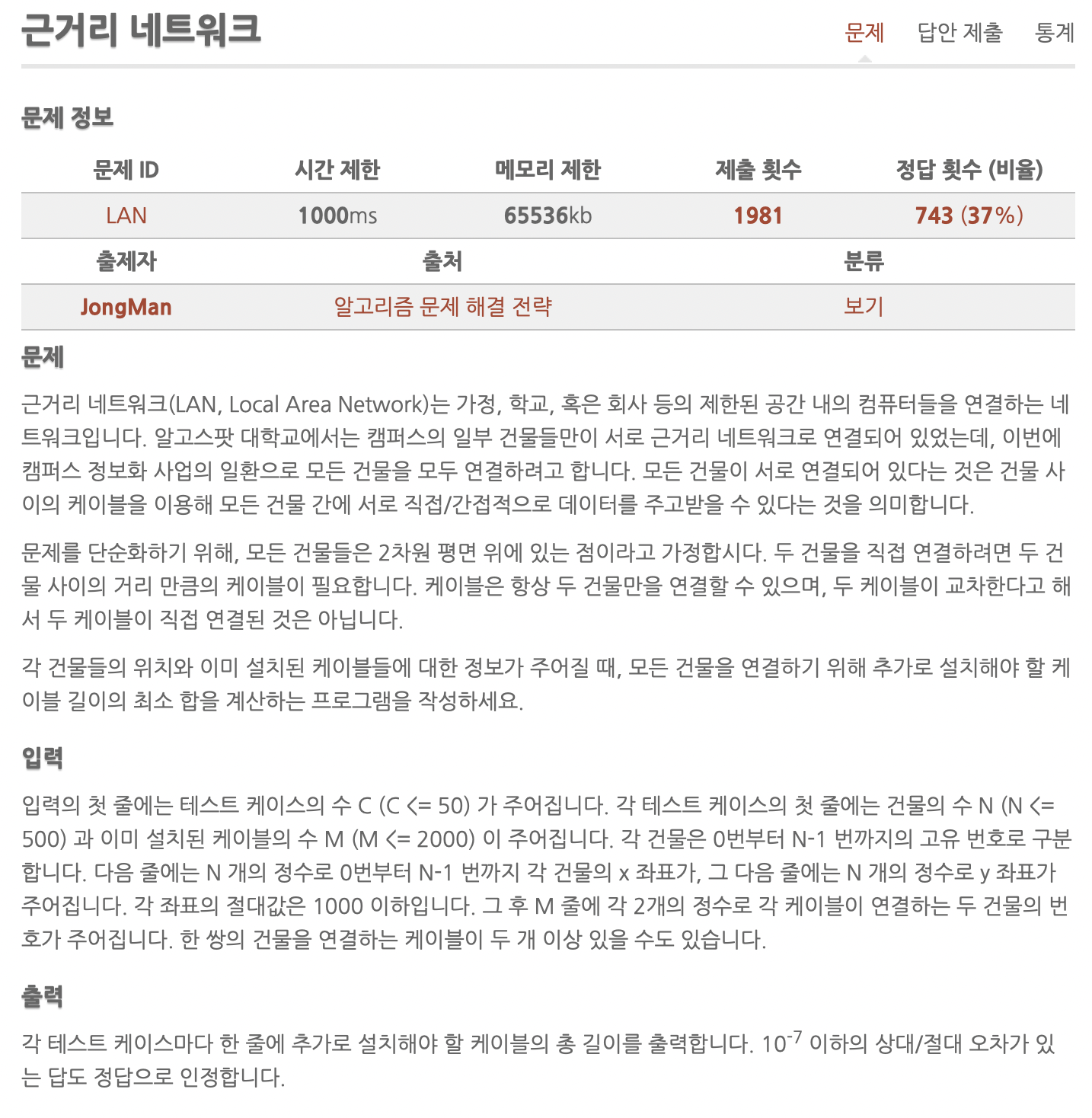
근거리 네트워크 문제 정보 문제 근거리 네트워크(LAN, Local Area Network)는 가정, 학교, 혹은 회사 등의 제한된 공간 내의 컴퓨터들을 연결하는 네트워크입니다. 알고스팟 대학교에서는 캠퍼스의 일
algospot.com
최소 스패닝 트리
문제 설명
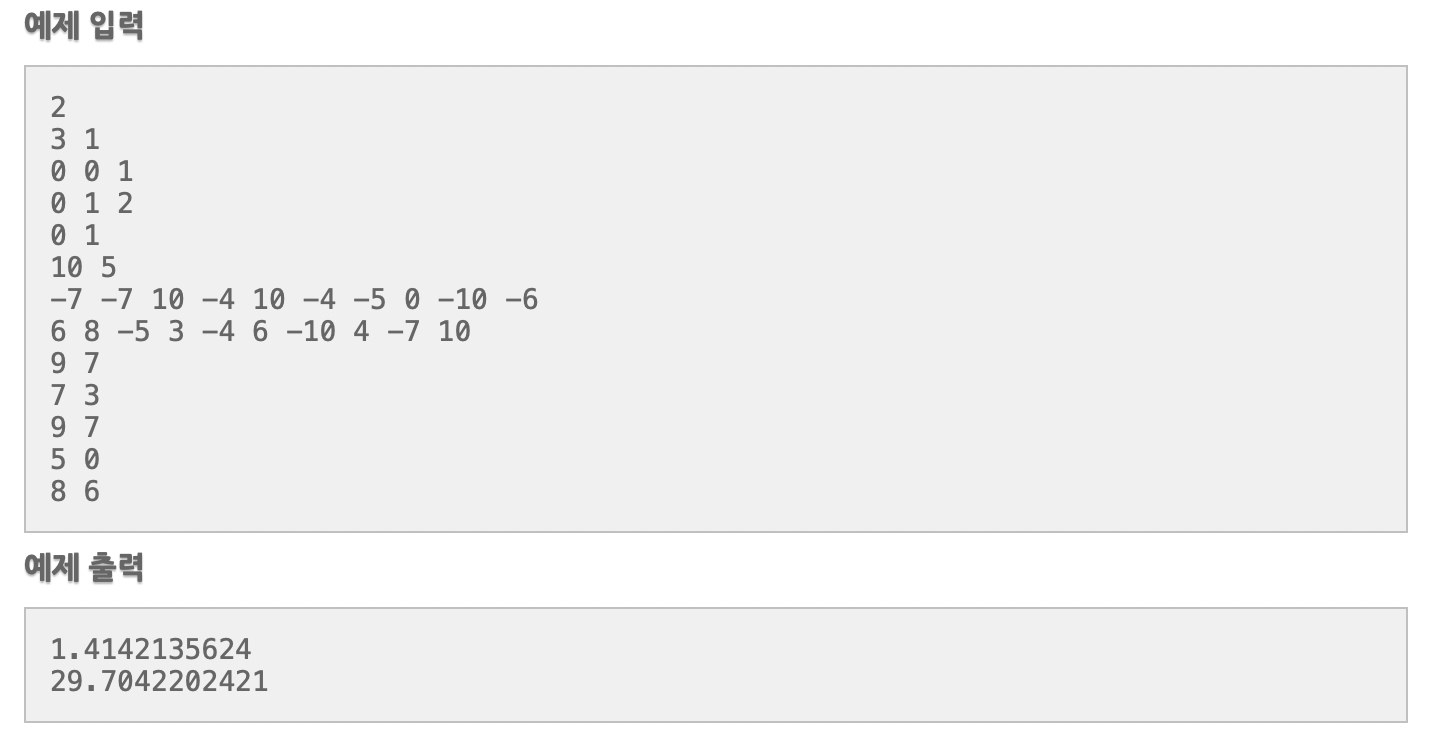
N개의 정점의 좌표가 주어지고 가중치 없이 연결할 수 있는 정점의 번호가 주어진다.
양방향 간선이지만 u에서 v로 가는 간선 하나만 저장해주면 된다. (u < v)
2중 for문을 통해서 모든 정점끼리 연결될 수 있는 가중치가 포함된 간선을 구해준다.
크루스칼 알고리즘을 적용하기 전에 주어지는 정점들을 Union해버리면 가중치 없이 정점을 미리 연결해줄 수 있다.
그리고 나머지 정점들을 크루스칼 알고리즘을 통해서 작은 가중치인 간선부터 탐색해 나간다.
일반적으론 지금까지 구한 정점의 개수가 N-1개가 될 때까지 알고리즘을 수행하지만 이번 문제는 처음에 간선을 미리 연결해놓았기 때문에 모든 간선을 돌아보면서 트리를 구성할 수 있는지 확인해보야야 한다.
코드
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#define fasti ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0);
#define fastio ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
#define INF 1e9+7
#define pii pair<int, int>
typedef long long ll;
// typedef pair<int, int> pii;
using namespace std;
struct Line{
double cost;
int st, ed;
};
int N, M;
vector<Line> Edge;
int Node[501];
bool compare(Line &a, Line &b){
return a.cost < b.cost;
}
int find_topnode(int a){
if(Node[a] < 0) return a;
return Node[a] = find_topnode(Node[a]);
}
bool Union_node(int a, int b){
a = find_topnode(a);
b = find_topnode(b);
if(a == b) return false;
if(Node[a] > Node[b]){
Node[b] += Node[a];
Node[a] = b;
}
else{
Node[a] += Node[b];
Node[b] = a;
}
return true;
}
double leng(double x1, double x2, double y1, double y2){
return sqrt(pow(x2 - x1, 2) + pow(y2 - y1, 2));
}
void input(){
Edge.clear();
memset(Node, -1, sizeof(Node));
cin >> N >> M;
double xarr[501], yarr[501];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
cin >> xarr[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
cin >> yarr[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < N-1; i++){
for(int j = i+1; j < N; j++){
Edge.push_back({leng(xarr[i], xarr[j], yarr[i], yarr[j]), i, j});
}
}
sort(Edge.begin(), Edge.end(), compare);
int a, b;
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++){
cin >> a >> b;
Union_node(a, b);
}
}
void solve(){
double ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < Edge.size(); i++){
double cost = Edge[i].cost;
int u = Edge[i].st;
int v = Edge[i].ed;
if(Union_node(u, v)){
ans += cost;
}
}
printf("%.10f\n", ans);
}
int main(){
int test;
cin >> test;
while(test--){
input();
solve();
}
return 0;
}
|
cs |